| unit_11_review_-_key.docx | |
| File Size: | 18 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
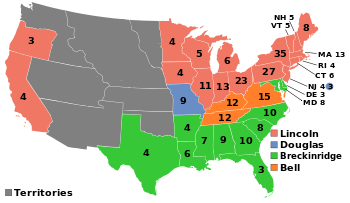
Election of 1860Information will be entered about the candidates and the election after class on Tuesday March 26th.
Here are the two videos from class on Tuesday, March 26th. Election of 1860 - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YMKbytk1QkE Aftermath of Election - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TGg5uDYHEQA |
Causes of the Civil War (Growth of Sectionalism)
Lincoln Douglas DebatesHere is the link to the video that we watched Monday about Abraham Lincoln and Stephen A. Douglas.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=we4DofhdJs0 | ||||||||
Pre-Civil War Events - From Class Notes
Henry Clay – known as the “Great Compromiser” for his efforts in the Missouri Compromise and the Comp. of 1850
John C. Calhoun - Believed strongly in the South having no need to compromise on the issue of slavery, if slavery is what the South wanted, slavery is what they should be able to have.
Daniel Webster – Supported the Compromise of 1850, wanted simply to preserve the Union.
3/5ths Compromise – First ever situation that arose over slavery; Slave populations would only count for 3/5ths of their totals, so that representation in Congress would be balanced.
Missouri Compromise – Compromise in the year 1820 over entrance of Missouri as a slave state. In order to balance the number of slave states and non-slave states, Maine entered as a state, as well as Missouri, in order to balance the number of states on each side of the slavery issue.
Compromise of 1850 – Issue arose over California becoming a state. Question was whether it would allow slavery or not. In order to appeal to the Northern (Anti-Slavery) states, Congress would allow California to enter as a free state. To please the Southern (Pro-Slavery) states, Congress would not pass any more laws about slavery in the territories won in the Mexican-American War. Additionally, Congress would pass a strict law helping recapture runaway slaves – known as the Fugitive Slave Act.
Kansas-Nebraska Act – The area known as Kansas Territory (remains of Louisiana Territory) would be divided into two areas – Kansas and Nebraska. People that moved there would vote on the issue of slavery – popular sovereignty – and this would decide the issue in the territories. This led to a mini civil war in Kansas known as Bleeding Kansas.
Fugitive Slave Act – 1850 law that helped owners recapture runaway slaves. The law allowed people of being accused of being runaways into custody, provided them with no trial, allowed a magistrate (judge) to rule on them being returned to their owner (received $10) or release them ($5).
Scott v. Sanford – Dred Scott sued for his freedom after his owner’s death. Decision went against Scott and in addition, extended slavery to the entire country by stating that slaves were the property of the owner and they could take their property with them any where they decided to go. A victory for the South.
John C. Calhoun - Believed strongly in the South having no need to compromise on the issue of slavery, if slavery is what the South wanted, slavery is what they should be able to have.
Daniel Webster – Supported the Compromise of 1850, wanted simply to preserve the Union.
3/5ths Compromise – First ever situation that arose over slavery; Slave populations would only count for 3/5ths of their totals, so that representation in Congress would be balanced.
Missouri Compromise – Compromise in the year 1820 over entrance of Missouri as a slave state. In order to balance the number of slave states and non-slave states, Maine entered as a state, as well as Missouri, in order to balance the number of states on each side of the slavery issue.
Compromise of 1850 – Issue arose over California becoming a state. Question was whether it would allow slavery or not. In order to appeal to the Northern (Anti-Slavery) states, Congress would allow California to enter as a free state. To please the Southern (Pro-Slavery) states, Congress would not pass any more laws about slavery in the territories won in the Mexican-American War. Additionally, Congress would pass a strict law helping recapture runaway slaves – known as the Fugitive Slave Act.
Kansas-Nebraska Act – The area known as Kansas Territory (remains of Louisiana Territory) would be divided into two areas – Kansas and Nebraska. People that moved there would vote on the issue of slavery – popular sovereignty – and this would decide the issue in the territories. This led to a mini civil war in Kansas known as Bleeding Kansas.
Fugitive Slave Act – 1850 law that helped owners recapture runaway slaves. The law allowed people of being accused of being runaways into custody, provided them with no trial, allowed a magistrate (judge) to rule on them being returned to their owner (received $10) or release them ($5).
Scott v. Sanford – Dred Scott sued for his freedom after his owner’s death. Decision went against Scott and in addition, extended slavery to the entire country by stating that slaves were the property of the owner and they could take their property with them any where they decided to go. A victory for the South.
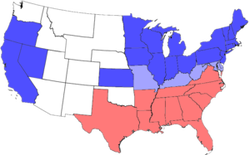
Order of Secession - (CSA)Confederate States of AmericaState Date of Secession
South Carolina December 20, 1860 Mississippi January 9, 1861 Florida January 10, 1861 Alabama January 11, 1861 Georgia January 19, 1861 Louisiana January 26, 1861 Texas February 1, 1861 *Lincoln's Inauguration - March 4th, 1861 *Fort Sumter - April 12th, 1861 - Civil War Begins Virginia April 17, 1861 Arkansas May 6, 1861 North Carolina May 20, 1861 Tennessee June 8, 1861 |
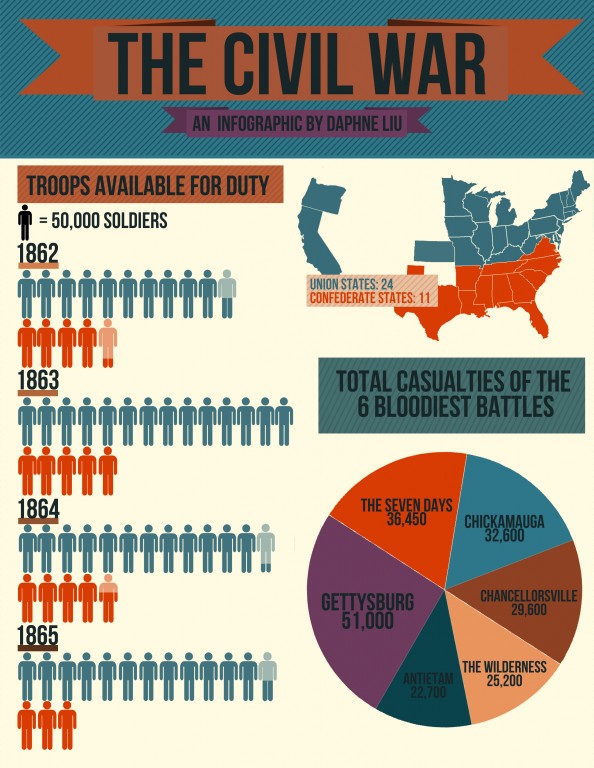
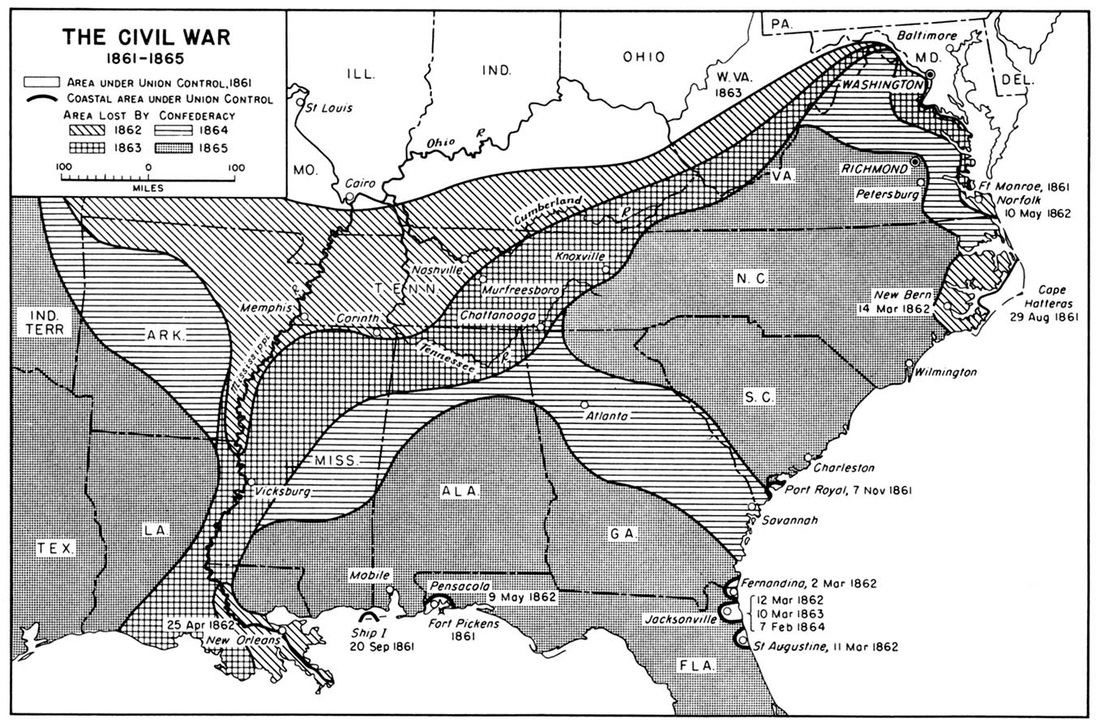
Important Events of the Civil WarFiring on Fort Sumter April 12-14, 1861
1st Battle of Bull Run July 21, 1861 Battle of Antietam September 17, 1862 Signing of the Emancipation Proclamation September 22, 1862; January 1, 1863 Battle of Gettysburg July 1-3, 1863 Siege of Vicksburg May 18 - July 4, 1863 Lee’s Surrender at Appomattox April 9, 1865 Assassination of Abraham Lincoln April 14, 1865 (Good Friday) |
Information on: North South
|
Ended on April 9th, 1865
Robert E. Lee Jefferson Davis To preserve the way of life the Southern states had become used to with an enslaved workforce 312,000 Confederacy, Gray, Rebels, Confederate States of America Richmond, VA Lost 30% 9 Million (9,000,000) 10 - 15% 29% 8% |
Links on Civil WarPlans and strategies - http://www.civilwarhome.com/strategyandtactics.htm
|
Videos about the Civil War
Very thorough video over the process/events of the Civil War - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y78zn1A4484
Another very thorough one as well, highlights Secession more than the one above - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1gfl6rHFUuQ
Interesting short video on what if the South had won the Civil War, it shows some battles going different that they actially did - https://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=50mD95cgcqE&feature=fvwp
Awesome Reconstruction Overview Video (we'll be covering this in Unit 12) - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_1KIENdWp5M
Another very thorough one as well, highlights Secession more than the one above - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1gfl6rHFUuQ
Interesting short video on what if the South had won the Civil War, it shows some battles going different that they actially did - https://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=50mD95cgcqE&feature=fvwp
Awesome Reconstruction Overview Video (we'll be covering this in Unit 12) - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_1KIENdWp5M